Since the creation of Bitcoin, most cryptocurrencies have been an alternative to transcend the traditional financial system. However, some central banks worldwide have recognized the importance of digital coins. Let’s see which countries have decided to create their CBDCs: Central Bank Digital Currencies.
CBDC is the answer of traditional financial institutions to blockchain technology. The CBDCs are similar to cryptocurrencies. But, their issuer controls them completely. Theoretically, these digital currencies serve as a medium of exchange and store of value.
Avant: the world’s first CBDC
Contrary to popular opinion, the first attempt at CBDC came long before blockchain technology arrived. 그만큼 Avant smart card system created by the Bank of Finland in the 1990s was the world’s first CBDC.

Avant cards featured smart card technology similar to that currently used in debit and credit cards. Although the Bank of Finland developed the system for three years, they sold Avant to commercial banks later. Once debit cards became less expensive and were upgraded to smart card technology, Avant became obsolete and went out of business.
The Avant system was operational until 2006 but never gained wide public acceptance. Mainly because there were fees for recharging or using the balance, making it expensive in the long run.
Countries with functioning CBDCs
Currently, two countries have launched their CBDCs: the Bahamas and Jamaica.
The Sand Dollar: The Bahamas CBDC
The Bahamas became the first of the countries to launch modern CBDCs in 2020. Since the land has only around 400,000 inhabitants, the process was quite fast. Mainly, this CBDC was born due to the difficulty of installing ATMs and bank offices on all the 700 country’s islands.

The Sand Dollar seeks to modernize and optimize the financial system of the Bahamas. In addition, it tries to reduce the costs of providing services and increase transactional efficiency. According to the International Monetary Fund (IFM), the main challenge facing the Sand Dollar today is the financial education of citizens.
Users agree with the IFM regarding the lack of education:
The Sand Dollar is having difficulty gaining traction. This is due to a lack of promotion and education of it. Persons on the family islands would need it more than persons in New Providence, Grand Bahama and other islands that have banking institutions.
The need is there and it is backed by the Central bank so I would trust it.
Dwayne Adderley, University of Michigan.
Interestingly, the name of this CBDC comes from the clipeasteroids. Better known as Sand Dollars, they are a crustacean inhabiting the island.
Jam-Dex: CBDC for Financial Inclusion in Jamaica
Jamaican Decentralized Exchange (Jam-Dex) is the second CBDC already working and has been available since June this year. This is another of the CBDCs launched by countries to improve financial inclusion. It is worth noting that Jamaica’s economy is primarily cash-based, so the Jam-Dex seeks Jamaica’s transition to a digital economy. But, unlike the Bahamian Sand Dollar, the Jam-Dex does not run on Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
Since August of last year, Jam-Dex has been undergoing pilot testing. Thus, they distributed the equivalent of $16 to each test participant.
Also, this CBDC works under a hybrid distribution model. The Central Bank of Jamaica will issue Jam-Dex to commercial banks and other authorized financial institutions. These entities will distribute the currency to the retail market.
Although the government created this CBDC to increase financial inclusion, users are concerned about the censorship power that governments could acquire:
다른 countries are planning to launch their CBDC
에 따르면 CBDC Tracker, over 100 countries currently have a pilot, proof of concept, research, and canceled CBDCs status. In addition to the two CBDCs that have already been successfully launched.
Among the countries that are piloting their CBDCs, we find 중국. Since 2020 the digital yuan has been tested, but cryptocurrencies are still prohibited in the territory. For this reason, the digital yuan does not use DLT either.
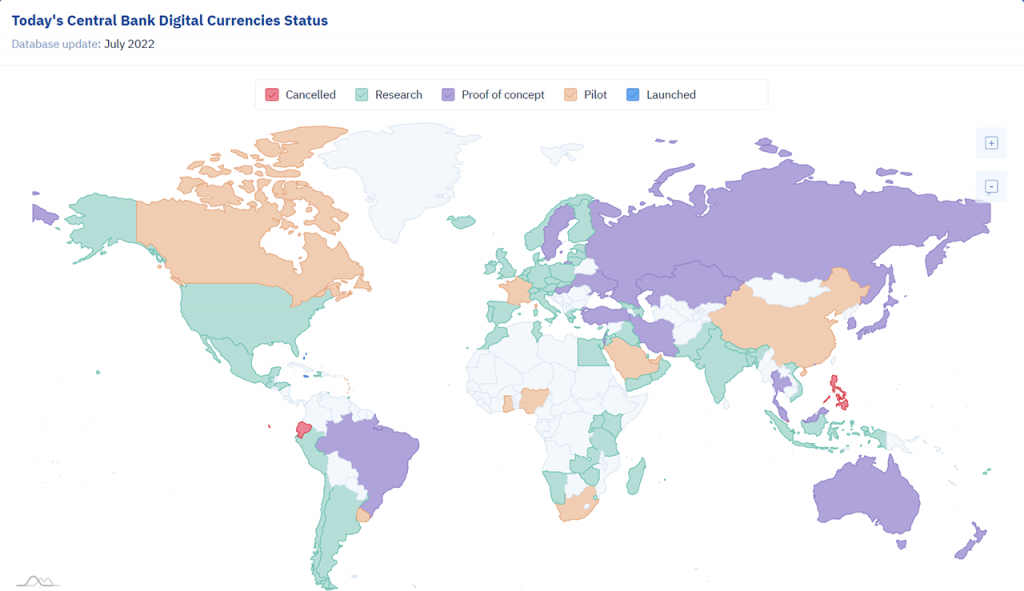
Countries such as France, Nigeria, Canada, and South Africa are also running a pilot test. And Taiwan, South Korea, Israel, Iran, Brazil, Japan, Russian Federation, Thailand, and Ukraine are currently on a proof of concept of their CBDCs.
About 70 other territories are researching to launch their digital currencies. Also, Singapore, Ecuador, Denmark, Haiti, and the Philippines canceled projects around CBDCs.
Cryptocurrencies or CBDCs, which is better?
In theory, CBDCs seem like a noticeable upgrade to countries’ financial systems. By 2022, 90% of central banks worldwide are researching to create their CBDCs, according to the Bank for International Settlements (BIS). These currencies could be more beneficial for payments than traditional means (such as cash and electronic transfers).
For the BIS, a CBDC would provide continued access to central bank money, operational resilience, payment diversity, financial inclusion, easier fiscal transfers, and more effortless cross-border payments.

However, they inherit the main problem of traditional money: they lack freedom. With CBDCs, users do not own their money, which the central bank controls. Thus, unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum (ETH), CBDCs are susceptible to government censorship and bans. Let’s not forget that central banks can decide when to cancel the project or increase costs, as in the Avant smart card system case.
We know of cases in which bad decisions by governments could harm the financial system, along with a decrease in economic activity and employment. That is another of the dangers faced by countries that undertake the task of using their own CBDCs, according to the Bank Policy Institute (BPI).
Wanna trade Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH) and other tokens? You can do it 안전하게 Alfacash에서! 그리고 우리가 소셜 미디어에서 이것과 다른 많은 것들에 대해 이야기하고 있다는 것을 잊지 마십시오.